
Dental Extractions
The removal of grossly damaged, unwanted, supernumerary, retained or impacted teeth from the oral cavity is referred to as ‘Extraction’ in dentistry. Depending upon the state, position and location of the tooth in the arch, the extraction can either be simple or surgical.
Simple extractions refer to those procedures in which a tooth is removed from its socket with the help of simple instruments such as forceps and elevators. Surgical incisions and flaps are not required to gain access to the tooth, which is easily visible and accessible in the oral cavity. Local anesthesia is administered at the site and after the numbness has set in, the tooth is carefully removed without damaged the surrounding soft tissues. A pressure pack or sutures may be used at the end of the procedure to control bleeding and to promote rapid healing of the socket.
 During a surgical extraction however, a different set of instruments are used to remove a tooth from the arch. In this case, the surgeon may need to create flaps and incisions to fully expose the tooth in the soft tissue. An example of surgical extraction procedures includes wisdom tooth impactions. Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, are the last ones to erupt in the oral cavity and therefore have very limited space. In majority of the cases, these teeth are impacted and cause the patient a great deal of discomfort in the form of pain, swelling and the inability to chew from the affected side. Nerve blocks are generally administered prior to surgical extractions to eliminate any chances of pain during the procedure.
During a surgical extraction however, a different set of instruments are used to remove a tooth from the arch. In this case, the surgeon may need to create flaps and incisions to fully expose the tooth in the soft tissue. An example of surgical extraction procedures includes wisdom tooth impactions. Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, are the last ones to erupt in the oral cavity and therefore have very limited space. In majority of the cases, these teeth are impacted and cause the patient a great deal of discomfort in the form of pain, swelling and the inability to chew from the affected side. Nerve blocks are generally administered prior to surgical extractions to eliminate any chances of pain during the procedure.
Some of the reasons why teeth may be extracted from the oral cavity include:
- Dental impactions
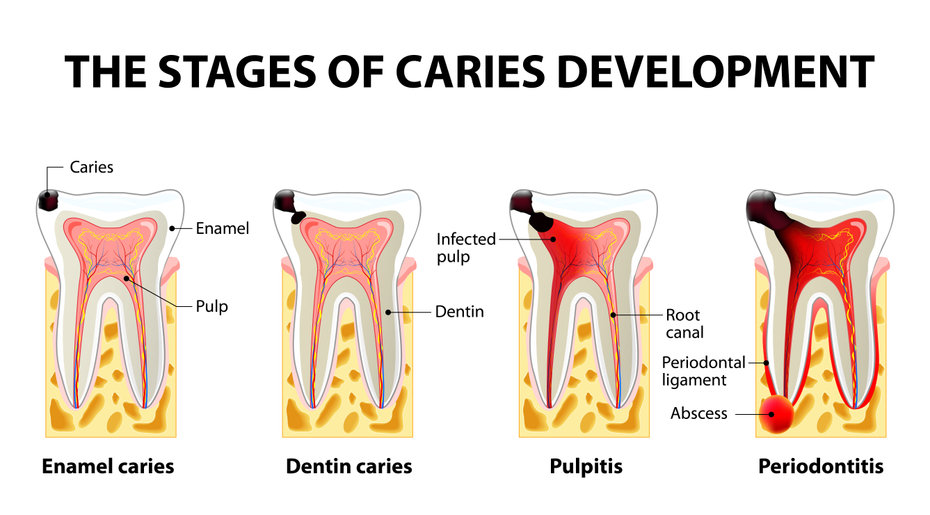
- Grossly carious or damaged teeth which cannot be restored
- Vertically fractured teeth
- Complex and root fractures
- To gain extra space for orthodontic treatments
- Retained deciduous/milk teeth
- Supernumerary/extra teeth
- Teeth with significant (grade 2 or 3) mobility due to gingival diseases such as Periodontitis
Call us today to book a consultation appointment with George Turner DDS or fill out our form below.
